Dealing with Rows and Columns
Dealing with Rows and Columns in Pandas DataFrame
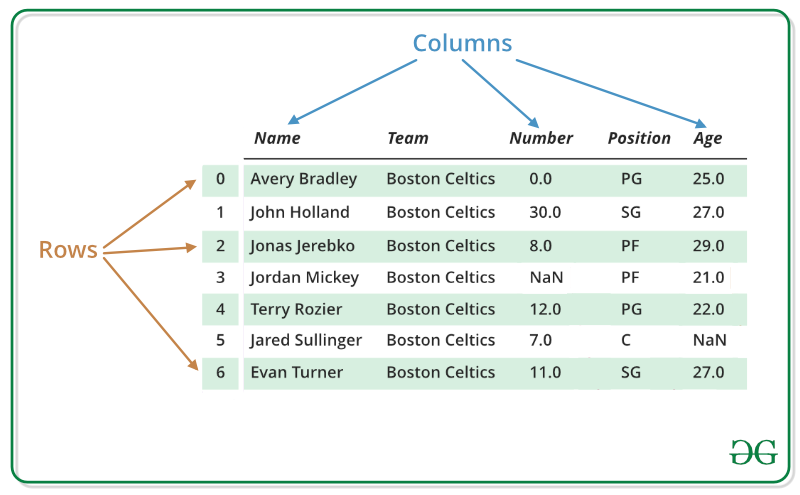
A Data frame is a two-dimensional data structure, i.e., data is aligned in a tabular fashion in rows and columns. We can perform basic operations on rows/columns like selecting, deleting, adding, and renaming. In this article, we are using nba.csv file.
Dealing with Columns
In order to deal with columns, we perform basic operations on columns like selecting, deleting, adding and renaming.
Column Selection:
In Order to select a column in Pandas DataFrame, we can either access the columns by calling them by their columns name.
# Import pandas package
import pandas as pd
# Define a dictionary containing employee data
data = {'Name':['Jai', 'Princi', 'Gaurav', 'Anuj'],
'Age':[27, 24, 22, 32],
'Address':['Delhi', 'Kanpur', 'Allahabad', 'Kannauj'],
'Qualification':['Msc', 'MA', 'MCA', 'Phd']}
# Convert the dictionary into DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
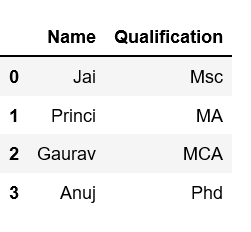
# select two columns
print(df[['Name', 'Qualification']])
Output:
For more examples refer to How to select multiple columns in a pandas dataframe
Column Addition:
In Order to add a column in Pandas DataFrame, we can declare a new list as a column and add to a existing Dataframe.
# Import pandas package
import pandas as pd
# Define a dictionary containing Students data
data = {'Name': ['Jai', 'Princi', 'Gaurav', 'Anuj'],
'Height': [5.1, 6.2, 5.1, 5.2],
'Qualification': ['Msc', 'MA', 'Msc', 'Msc']}
# Convert the dictionary into DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
# Declare a list that is to be converted into a column
address = ['Delhi', 'Bangalore', 'Chennai', 'Patna']
# Using 'Address' as the column name
# and equating it to the list
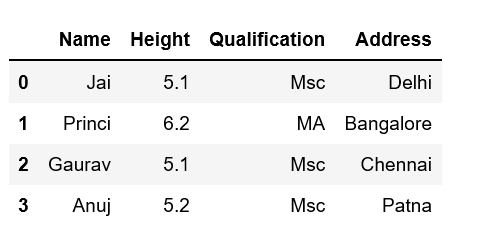
df['Address'] = address
# Observe the result
print(df)
Output:
For more examples refer to Adding new column to existing DataFrame in Pandas
Column Deletion:
In Order to delete a column in Pandas DataFrame, we can use the drop() method. Columns is deleted by dropping columns with column names.
# importing pandas module
import pandas as pd
# making data frame from csv file
data = pd.read_csv("nba.csv", index_col ="Name" )
# dropping passed columns
data.drop(["Team", "Weight"], axis = 1, inplace = True)
# display
print(data)
Output:
As shown in the output images, the new output doesn’t have the passed columns. Those values were dropped since axis was set equal to 1 and the changes were made in the original data frame since inplace was True.
Data Frame before Dropping Columns-
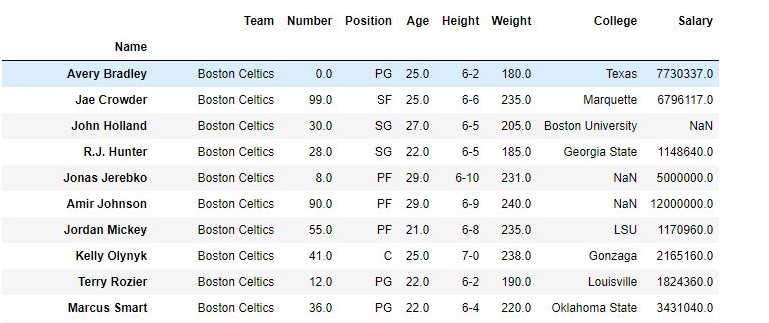
Data Frame after Dropping Columns-
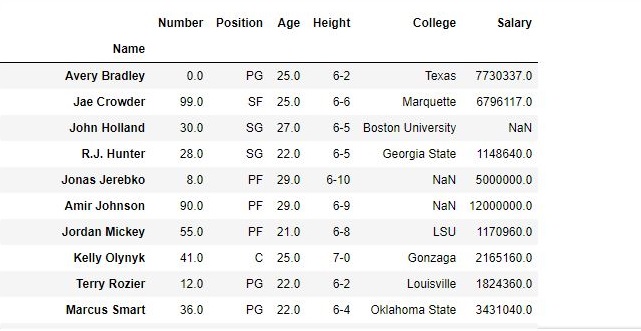
For more examples refer to Delete columns from DataFrame using Pandas.drop()
Dealing with Rows:
In order to deal with rows, we can perform basic operations on rows like selecting, deleting, adding and renmaing.
Row Selection:
Pandas provide a unique method to retrieve rows from a Data frame.[DataFrame.loc[]](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/python-pandas-extracting-rows-using-loc/) method is used to retrieve rows from Pandas DataFrame. Rows can also be selected by passing integer location to an iloc[] function.
# importing pandas package
import pandas as pd
# making data frame from csv file
data = pd.read_csv("nba.csv", index_col ="Name")
# retrieving row by loc method
first = data.loc["Avery Bradley"]
second = data.loc["R.J. Hunter"]
print(first, "\n\n\n", second)
Output:
As shown in the output image, two series were returned since there was only one parameter both of the times.
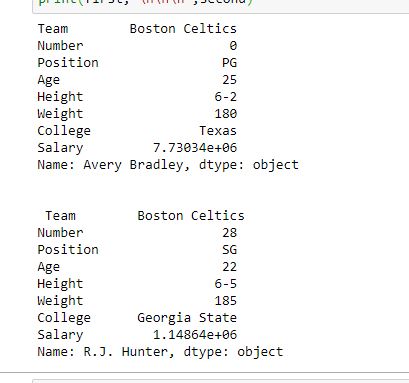
For more examples refer to Pandas Extracting rows using .loc[]
Row Addition:
In Order to add a Row in Pandas DataFrame, we can concat the old dataframe with new one.
# importing pandas module
import pandas as pd
# making data frame
df = pd.read_csv("nba.csv", index_col ="Name")
df.head(10)
new_row = pd.DataFrame({'Name':'Geeks', 'Team':'Boston', 'Number':3,
'Position':'PG', 'Age':33, 'Height':'6-2',
'Weight':189, 'College':'MIT', 'Salary':99999},
index =[0])
# simply concatenate both dataframes
df = pd.concat([new_row, df]).reset_index(drop = True)
df.head(5)
Output:
Data Frame before Adding Row-
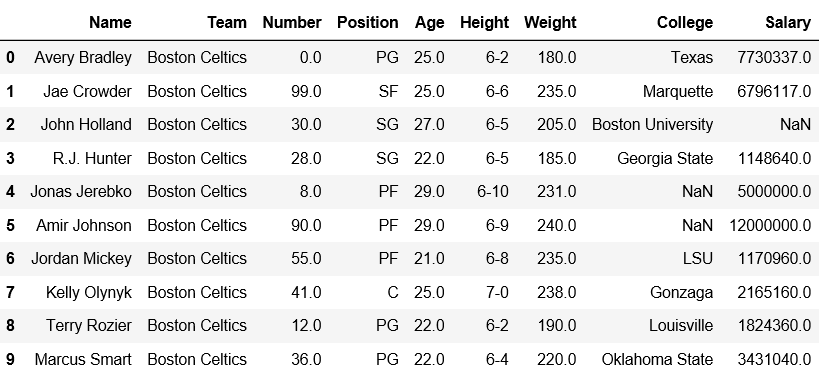
Data Frame after Adding Row-
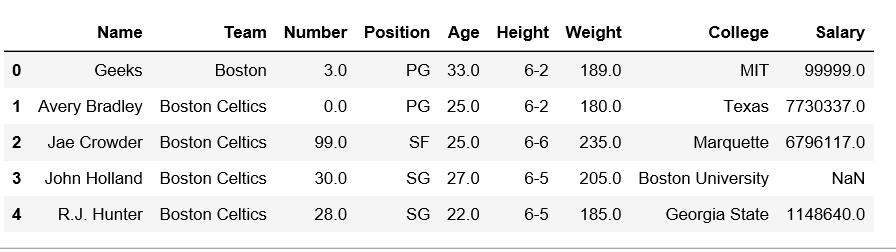
For more examples refer to Add a row at top in pandas DataFrame
Row Deletion:
In Order to delete a row in Pandas DataFrame, we can use the drop() method. Rows is deleted by dropping Rows by index label.
# importing pandas module
import pandas as pd
# making data frame from csv file
data = pd.read_csv("nba.csv", index_col ="Name" )
# dropping passed values
data.drop(["Avery Bradley", "John Holland", "R.J. Hunter",
"R.J. Hunter"], inplace = True)
# display
data
Output:
As shown in the output images, the new output doesn’t have the passed values. Those values were dropped and the changes were made in the original data frame since inplace was True.
Data Frame before Dropping values-
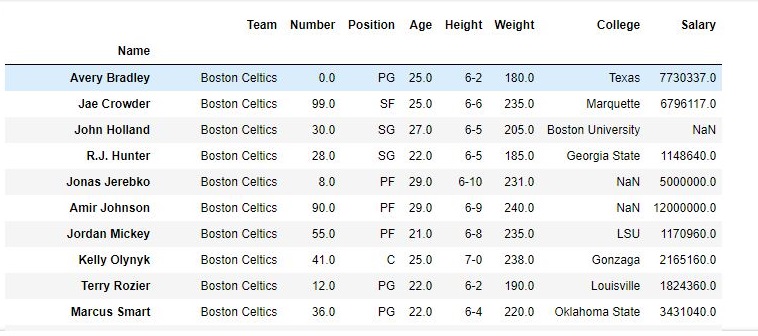
Data Frame after Dropping values-
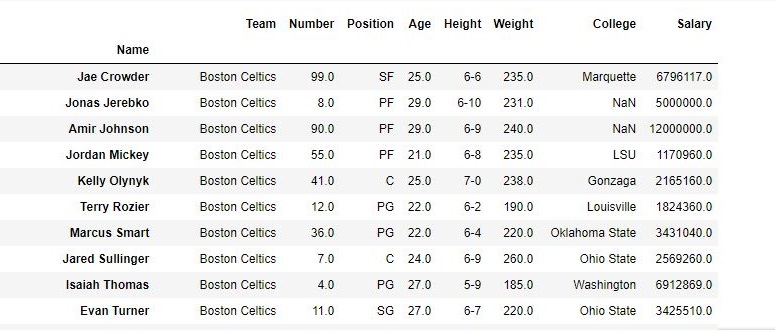
For more examples refer to Delete rows from DataFrame using Pandas.drop()
Problem related to Columns:
- How to get column names in Pandas dataframe
- How to rename columns in Pandas DataFrame
- How to drop one or multiple columns in Pandas Dataframe
- Get unique values from a column in Pandas DataFrame
- How to lowercase column names in Pandas dataframe
- Apply uppercase to a column in Pandas dataframe
- Capitalize first letter of a column in Pandas dataframe
- Get n-largest values from a particular column in Pandas DataFrame
- Get n-smallest values from a particular column in Pandas DataFrame
- Convert a column to row name/index in Pandas
Problem related to Rows:
Reference : https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/dealing-with-rows-and-columns-in-pandas-dataframe/